Choosing the right GMRS frequencies is essential for effective communication in various scenarios, whether you're in a bustling city or exploring the great outdoors. The General Mobile Radio Service (GMRS) provides a unique set of frequencies designated for personal use, enabling users to maintain clear and reliable communication over considerable distances. However, with a range of channels available, understanding how to select the most suitable GMRS frequencies for your specific needs can significantly enhance your communication experience.
In this guide, we will delve into the factors to consider when choosing GMRS frequencies, such as your intended use, the environment in which you will be operating, and the equipment available to you. Effective frequency selection not only helps in achieving optimal signal clarity but also minimizes interference with other users, ensuring your conversations remain private and uninterrupted. By understanding the intricacies of GMRS frequencies, you can make informed decisions that cater to your communication requirements, ultimately improving your overall connectivity and coordination in various activities or emergencies.

When considering GMRS (General Mobile Radio Service) frequencies for your communication needs, it's essential to understand both the frequency ranges and the specific applications they serve. GMRS operates within the UHF band, primarily between 462 MHz and 467 MHz, which allows for reliable communication over varying distances. This frequency range is advantageous for users seeking clear audio communication in environments with obstructions, such as urban areas or dense forests.
Different GMRS frequencies are allocated for specific uses, including simplex and repeater operations. Simplex frequencies are commonly used for direct point-to-point communication, making them ideal for personal or small group use, such as family outings or neighborhood communications. Repeater frequencies, on the other hand, enable extended range by allowing signals to be transmitted further through a network of repeaters. This application is particularly beneficial for organizations or events that require broad coverage, such as outdoor events or emergency response coordination.
Choosing the right GMRS frequencies involves understanding the terrain, desired communication range, and the number of users. For example, if operating in a rural area, utilizing repeater frequencies can significantly enhance communication capabilities. Conversely, in a more local and compact setting, simplex frequencies may suffice. By aligning frequency selection with specific needs, users can optimize their GMRS communication experience for reliability and clarity.
| Frequency (MHz) | Bandwidth (kHz) | Typical Use Case | Range (Miles) | License Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 462.550 | 12.5 | General Communication | 2-5 | Yes |
| 462.575 | 12.5 | Outdoor Recreation | 2-5 | Yes |
| 462.600 | 12.5 | Emergency Services | 5-10 | Yes |
| 462.625 | 12.5 | Business Operations | 5-10 | Yes |
| 462.650 | 12.5 | Personal Communication | 2-5 | Yes |
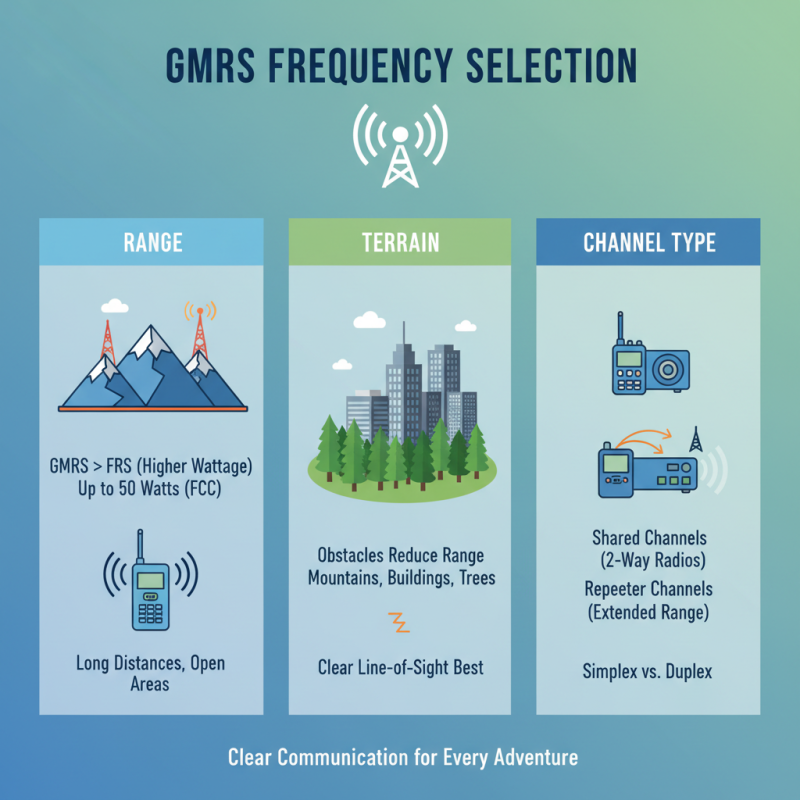
When selecting the right GMRS (General Mobile Radio Service) frequencies for your communication needs, it is crucial to consider several essential factors that can significantly impact the effectiveness and clarity of your communication. One key factor is the range you require. GMRS channels can provide better range than FRS (Family Radio Service) due to the higher wattage allowed under GMRS regulations. According to the FCC, GMRS radios can transmit up to 50 watts of power. This increased power enables clearer signals, especially over long distances in open areas, making it an ideal choice for outdoor activities or emergencies.
Another important consideration is the potential for interference with other radio users. GMRS operates on specific frequencies, and crowded channels can lead to disruptions. Understanding the typical usage patterns on certain channels, as indicated by studies from the ARRL (American Radio Relay League), can help you select the best channels that remain less congested. Selecting channels that are less frequently used or that have fewer active users will enhance your communication reliability.
Lastly, assessing the addition of privacy codes can enhance your communication by minimizing interference from other parties. Utilizing sub-audible tones allows users to communicate without interruption from adjacent users on shared frequencies, a common concern noted in various communication studies. By taking these factors into account, you can select the GMRS channels that best suit your specific communication requirements and ensure more effective and efficient radio use.
When selecting GMRS frequencies, regulatory considerations play a crucial role in ensuring compliance and optimal communication. The General Mobile Radio Service (GMRS) is regulated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States, and it requires users to obtain a license to operate. This is essential because GMRS frequencies operate within a specific bandwidth allocated by the FCC, primarily within the UHF range, typically between 462.550 MHz and 467.725 MHz. Understanding these regulations is vital for both amateur radio operators and businesses relying on GMRS for communication.
Moreover, frequency selection should account for the allowed transmission power, which can reach up to 50 watts for mobile units, facilitating extended communication range. According to a 2021 industry report from the National Association of Broadcasters, the effective use of GMRS frequencies can significantly enhance communication efficiency, particularly in rural areas where traditional cellular networks may falter. It’s also important to be aware of the limitations, as GMRS communications may not cross state lines if licensed only for local use. Navigating these regulations carefully not only prevents legal issues but also ensures that users can effectively leverage GMRS for their communication needs.
When selecting the right GMRS frequencies for your communications, understanding the range and power requirements is crucial. GMRS, or General Mobile Radio Service, operates on frequencies between 462 MHz and 467 MHz, allowing users to communicate over distances that can vary significantly depending on their setup. According to a recent report by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), GMRS radios can transmit at power levels up to 50 watts under specific conditions, which can dramatically improve range compared to other services like FRS (Family Radio Service). However, real-world distances vary based on terrain, antenna quality, and height, with typical ranges of 5 to 10 miles in urban areas and up to 30 miles in open areas.
Tips: When selecting your GMRS frequencies, assess your communication needs carefully. If your intended use primarily involves short-range communication in densely populated areas, lower power settings may suffice. On the other hand, if you need to cover longer distances in rural settings, investing in higher wattage equipment with superior antennas can significantly enhance your reach.
The importance of range and power also extends to the weather conditions and the geographical features of the area where you will be operating. Studies have shown that natural barriers like mountains and urban structures can severely impact signal propagation. It’s advisable to conduct field tests in different conditions to determine the practical communication capabilities of your GMRS setup. This hands-on approach, combined with a thorough understanding of your power options, will ensure you choose the most effective GMRS frequencies for your needs.
When managing GMRS frequencies, it is essential to prioritize communication clarity and efficiency. Start by assessing your communication needs: consider factors such as the size of your group, the terrain you will be covering, and the types of activities you will be involved in. Select frequencies that minimize interference from other users, while also ensuring that your chosen channels offer adequate range.
Utilizing repeater systems, if available, can enhance your coverage and extend the effective communication distance.
Maintaining a frequency management strategy is equally important. Keep a record of the frequencies in use, noting which channels work best under various conditions. Encourage all users within your group to adhere to established protocols for switching frequencies when interference occurs, and remind them to practice good etiquette by allowing others to use the channels.
Regular training sessions can help reinforce the importance of these practices and ensure that everyone is familiar with the communication tools and techniques necessary for optimal usage.